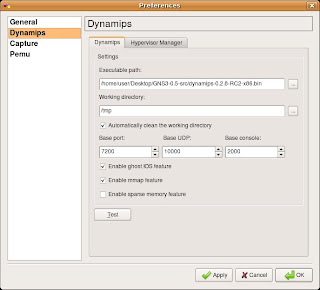
SIMPLY CHECK OR TICK SPARSEMEM WHICH IS NOT TICK BY DEFAULT IN THE GNS3 SECTION
THE REASON BEHIND THIS IS AS FOLLOWS ....
Memory Usage Labs can consume a large amount of real and virtual memory. The “ghostios” and “sparemem” options were added to address both of these issues, respectively.
The Ghostios option can significantly reduce the amount of real host RAM needed for labs with multiple routers running the same IOS image. With this feature, instead of each virtual router storing an identical copy of IOS in its virtual RAM, the host will allocate one shared region of memory that they will all utilize. So for example, if you are running 10 routers all with the same IOS image, and that image is 60 MB in size you will save 9*60 = 540 MB of real RAM when running your lab. Ghostios is enabled, by default, in GNS3.
The “sparsemem” feature does not conserve real memory, but instead reduces the amount of virtual memory used by your router instances. This can be important, because your OS limits a single process to 2 GB of virtual memory on 32-bit Windows, and 3 GB on 32-bit Linux. Enabling sparsemem only allocates virtual memory on the host that is actually used by the IOS in that router instance, rather than the entire amount of RAM configured. This can allow you to run more instances.
Both features rely on mmap, so this must also be enabled. Select Preferences under the Edit menu within GNS3. Check the appropriate boxes to enable these features.
CREDIT GOES TO MIKE